Diabetes can affect many parts of the body, and the eyes are no exception. One of the most serious eye complications of diabetes is diabetic retinopathy, which can progress to Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) and Diabetic Macular Edema (DME). These conditions are leading causes of vision loss in people with long-standing diabetes—but early diagnosis and modern treatments can help protect eyesight.
What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy?
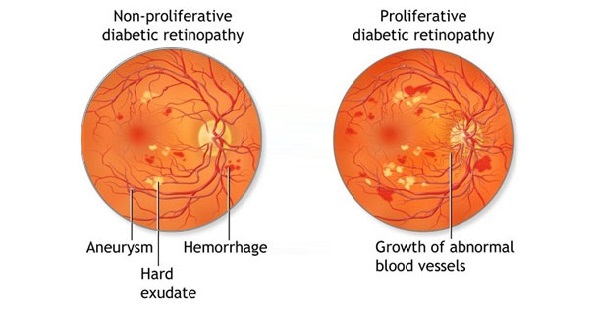
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when prolonged high blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels of the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. These damaged vessels may leak fluid, close off, or grow abnormally. Poor blood sugar control, long duration of diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol increase the risk.
As the condition worsens, it may lead to PDR and DME.
What Is Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)?
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy is an advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy. When the retina does not receive enough oxygen, it responds by growing new blood vessels. Unfortunately, these new vessels are weak and abnormal.
Complications of PDR include:
- Sudden bleeding inside the eye (vitreous hemorrhage)
- Severe and sudden vision loss
- Scar tissue formation
- Retinal detachment
- Permanent blindness if untreated
PDR often develops without warning symptoms, making regular diabetic eye exams extremely important.
What Is Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)?
Diabetic Macular Edema occurs when fluid leaks into the macula—the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. Swelling of the macula leads to blurred or distorted central vision.
Common symptoms include:
- Blurry vision
- Difficulty reading or recognizing faces
- Wavy or distorted straight lines
- Dull or faded colors
DME can occur at any stage of diabetic retinopathy and is a major cause of vision impairment in diabetic patients.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Both PDR and DME can progress silently. Many patients have no symptoms until vision loss occurs. Regular diabetic eye screening allows early detection and timely treatment, significantly reducing the risk of permanent vision loss.
Newer Treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy and Macular Edema
Modern ophthalmology offers highly effective treatments to control diabetic eye disease.
Anti-VEGF Eye Injections
These injections reduce leakage and abnormal blood vessel growth. Benefits include:
- Reduction of macular swelling
- Prevention of vision loss
- Stabilization or improvement of vision
The procedure is quick, safe, and performed under local anesthesia.
Laser Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy
Laser therapy helps by:
- Sealing leaking blood vessels
- Reducing abnormal vessel growth
- Lowering the risk of severe vision loss in PDR
Advanced laser technology allows precise and customized treatment.
Final Takeaway
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema are serious diabetic eye complications—but they are treatable. With regular eye check-ups, good diabetes control, and modern treatments like injections and laser, vision can often be preserved for life.
👁️ If you have diabetes, routine eye examinations are essential. Early action today protects your vision tomorrow.